What mortgage loan can I get? 5 types of home loans
Getting a loan may seem like a straightforward process, but it can get quite confusing. With so many options available, such as conforming loans, non-conforming loans, and jumbo loans, it’s easy to get lost in the details. Choosing the right type of loan can have a significant impact on your interest rate and down payment requirements.
If you are wondering which mortgage loan is the best for you, this will depend on your specific mortgage applicant profile. Whether you’re a first-time home buyer, looking to downsize, or interested in refinancing, there is a loan that will fit your unique situation.
1. Conventional Mortgages
The most common type of home loan is conventional mortgages. However, it’s important to note that these loans may require specific criteria for a borrower’s credit score and debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, which differs from other loan options. Typically, a minimum credit score of 620 and a DTI ratio of 50% is needed to qualify for a conventional mortgage.
Characteristics:
- If you are a first-time home buyer, you can buy a home with as little as 3% down.
- If you already own a home your down payment will be 5%
- You need a credit score of at least 620.
- You can skip PMI if you have a down payment of at least 20%
- Borrowers with a DTI of 50% or less can typically benefit from conventional loans.
Conventional loans are a great option for borrowers who can afford larger down payments, as they offer lower interest rates.

2. Fixed-rate mortgage
A fixed-rate mortgage maintains a consistent interest rate and principal/interest payment over the entire loan term. While your monthly expenses might vary because of fluctuations in property taxes and insurance costs, fixed-rate mortgages predominantly provide a highly foreseeable and stable monthly payment.
- It’s a better option if you’re living in your “forever home.”
- You will want to avoid this type of mortgage if interest rates in your area are high.
- A fixed-rate mortgage can help you budget and plan for the long term.
3. Adjustable-rate mortgage
An adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) stands in contrast to a fixed-rate mortgage. ARMs are 30-year loans with interest rates that fluctuate in response to market rate changes.
When you commit to an ARM, you initially agree to a fixed interest rate during an introductory period, which commonly spans 5, 7, or 10 years. For instance, if you opt for a 5/1 ARM loan, you’ll enjoy a fixed interest rate for the initial 5 years. Throughout this introductory phase, your interest rate remains constant and typically offers a lower rate compared to 30-year fixed-rate mortgages.
After your introductory period ends, your interest rate may change depending on the current market interest rates. Your lender will use a specific index to measure these rate fluctuations. If the rates indicated by the index go up, your interest rate will also increase. On the other hand, if the index’s rates go down, your interest rate will decrease accordingly.
Adjustable-rate mortgages come with rate caps that put a limit on the maximum allowable adjustments to your interest rate during specific time frames and over the term of your loan. These rate caps act as a safeguard against sudden and significant increases in interest rates. For example, even if interest rates rise steadily over time when your loan reaches its rate cap, your interest rate will no longer increase. On the flip side, these rate caps also impose restrictions on how much your interest rate can decrease.
Characteristics:
- ARM is a good choice if you buy a starter home before moving to your forever home.
- These can be especially helpful if you plan to make extra payments towards your loan early on.
- During the full term of the loan, you can stay in your home with an ARM. ARMs can offer you this flexibility.
4. Government-backed loans
Loans that are backed by the government and insured by agencies like the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), Veterans Affairs (VA), or the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) offer a wider range of qualification options. Government-backed loans are a popular choice for borrowers who may not qualify for traditional loans, due to lower credit scores or insufficient income. These loans often have more lenient requirements, such as lower down payments, which make them a more accessible option for first-time home buyers. Additionally, government-backed loans offer competitive interest rates, which can help borrowers save money over the life of the loan. Overall, government-backed loans are a viable option for those who are looking to purchase a home and may not qualify for other types of loans.
FHA Loans
FHA loans are insured by the Federal Housing Administration and allow you to buy a home with a low credit score – as low as 580. A 3.5% down payment is required, but you may still qualify with a credit score as low as 500 by paying a 10% down payment.
USDA Loans
USDA loans are a great option for homebuyers. They are insured by the United States Department of Agriculture and offer lower mortgage insurance requirements than FHA loans. You can even buy a home without a down payment. However, you must meet income requirements and buy a home in an eligible suburban or rural area to qualify.
VA Loans
VA loans, insured by the Department of Veterans Affairs, offer a $0 down payment and lower interest rates than most loans. Service requirements in the Armed Forces/National Guard apply.

5. Jumbo Loans
A jumbo loan is a type of loan that exceeds the standard conforming loan limits applicable in your region. Typically, you’d require a jumbo loan when purchasing a high-value property.
When it comes to interest rates, jumbo loans usually have similar rates to conforming loans. However, qualifying for a jumbo loan is more difficult as it has stricter eligibility requirements than other loan options. To be eligible for a jumbo loan, you will need a higher credit score and a lower debt-to-income ratio (DTI).
Jumbo loans require a credit score of 700+, a larger down payment, cash reserves, and lower DTI compared to other loans. A significant down payment of 10-20% is typically necessary.
It’s essential to be aware that when it comes to determining your interest rate and the cost of mortgage insurance, the lowest median score is still the one used, potentially leading to a slightly higher interest rate for your loan. Furthermore, the practice of averaging credit scores is not applicable to all types of loans.
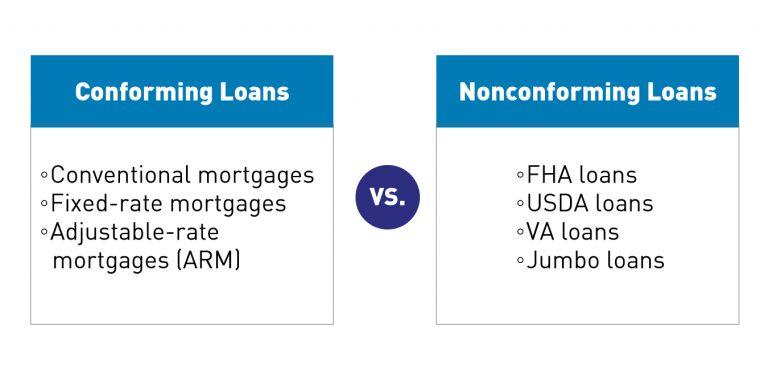
Difference between conforming and nonconforming loans
Mortgages can be classified as either conforming or nonconforming loans. The classification is based on whether the lender retains the loan, collecting payments and interest, or sells it to either Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac, two real estate investment companies.
Conforming Loans
A conforming loan is a conventional mortgage eligible for acquisition by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac. To be eligible for purchase by these entities, the mortgage must meet essential criteria established by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA). These criteria encompass the following loan requirements:
- Below the maximum dollar limit: The maximum dollar limit in most parts of the contiguous United States is $726,200 in 2023. In Alaska, Hawaii, and certain high-cost areas, the limit is $1,089,300. Higher limits also apply if you buy a multifamily unit. Your lender can’t sell your loan to Fannie or Freddie and you can’t get a conforming mortgage if your loan is more than the maximum amount, unless you qualify for a super conforming loan.
- Not a Federally Backed Loan: The loan must not already have backing from a federal government entity. Some government bodies, such as the Department of Veterans Affairs and the Federal Housing Administration, provide insurance on home loans. If your loan is government-backed, Fannie and Freddie may not purchase your mortgage.
- Meets Lender-Specific Criteria: To qualify for a conforming mortgage, your loan must meet the lender’s specific criteria. For instance, a credit score of at least 620 is typically required. Consideration of property guidelines and income limits may also be necessary when applying for a conforming loan. A Home Loan Expert can assess your unique financial situation to determine eligibility.
Conforming loans are characterized by clear-cut guidelines, reducing variability in loan qualification. Opting for a conforming loan could potentially result in securing a lower interest rate.
Nonconforming Loans
Nonconforming loans often feature broader qualification criteria compared to conforming loans, providing opportunities to secure financing with a lower credit score, access larger loan amounts, or obtain a loan without a down payment. In some cases, approval for a nonconforming loan may still be possible even with negative items on your credit report, such as bankruptcy. It’s worth noting that a majority of nonconforming loans are either government-backed loans or jumbo mortgages.

